Tree
1. Properties of trees
Forest: cycle이 없는 그래프
Tree: connected forest
예시) 4개의 tree로 구성된 forest
Thm 9.1
Let T be a graph with n vertices. Then the following are equivalent: (i) T is a tree; (ii) T contains no cycles, and has n-1 edges; (iii) T is connected, and has n-1 edges; (iv) T is connected, and each edge is a bridge (v) any two vertices of T are connected by exactly one path; (vi) T contains no cycles, but the addition of any new edge creates exactly one cycle.\
Corollary 9.2
G가 n개의 vertices와 k개의 component로 구성된 forest라면 G는 n-k개의 edge를 가지고 있는다.
Spanning Tree: 연결된 graph G가 있을 때, cycle 하나를 골라 edge들을 제거해나가면 tree인데 그래프 G의 모든 vertex를 담고 있는 graph를 만들 수 있다. 이때, 해당 tree를 spanning tree라고 부른다.
Spanning Forest: 임의의 graph G의 각 component들을 spanning tree로 만들면, 이 spanning tree로 구성된 전체 그래프를 spanning forest라고 부른다.
Cycle rank ($\gamma(G)$): 제거된 전체 edge 개수
$\gamma(G)$ = m - n + k
Cutset rank ($\xi(G))$: spanning forest의 전체 edge 수
$\xi(G))$ = n - k
Complement of a spanning forest T: 전체 그래프 G에서 T에 속하는 edge들을 제거한 것을 말한다.
Thm 9.3
만약 T가 그래프 G의 spanning forest라면, (i) G의 각 cutset은 T와 공통되는 edge를 가지고 있다. (ii) G의 각 cycle은 T의 complement와 공통되는 edge를 가지고 있다.
(ii) 증명: G의 cycle이 T의 complement와 공통되는 edge를 가지지 않는다면 G의 cycle은 T에 속해야 하는데, 이는 모순이다.
The fundamental set of cycles associated with T (fundamental set of cycles of G): G의 spanning tree들에 spanning tree에 속하지 않는 edge들을 추가해 unique한 cycle들을 만들 수 있다.
The fundamental set of cutset associated with T: G Spanning forest T가 있을 때, T의 edge를 제거하면 하나의 vertex set를 둘로 분리할 수 있다. 이때의 cutset들을 말한다.
2. Counting Trees
Cayley’s Thm
There are $n^{n-2}$ distinct labelled trees on n vertices.
증명
T(n, k): n개의 정점을 가진 graph에서 특정 vertex가 degree k를 가질 때 labelled tree의 개수
(n - k)T(n,k- 1) = (n - l)(k- l)T(n, k)를 보임.
T(n, n-1) = 1 이라는 사실에 기반해 T(n, k)를 n과 k만을 이용해 계산할 수 있도록 변경함.
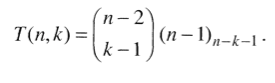
- T(n)은 특정 vertex의 degree가 1부터 n-1일 때까지의 합이라는 것을 이용해 T(n)을 유도함.
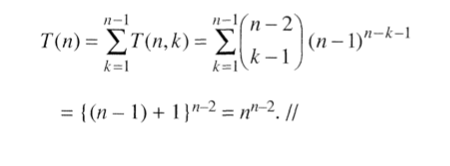
Corollary 10.2
완전 연결 그래프 $K_n$의 spanning tree의 개수는 $n^{n-2}$이다.
Matrix-tree thm
G가 vertex set ${v_1, …, v_n}$으로 구성되고 완전히 연결된 간단한 graph이고, $m_{ii} = deg(v_i), m_{ij}=-1$ if $v_i$ and $v_j$ are adjacent, and $m_{ij}=0$로 구성된 n x n 행렬 M이 있을 때, G의 spanning tree의 개수는 M의 아무 원소의 cofactor와 같다.
3. More applications
1) The minimum connector problem
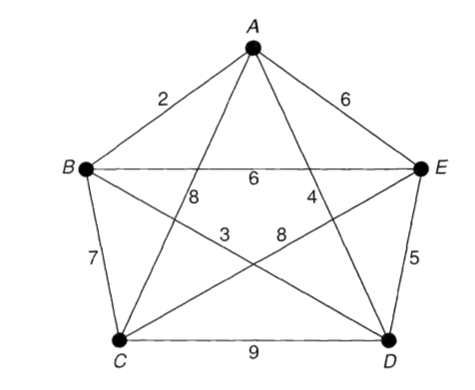
위와 같은 그래프에서 minimum spanning tree를 찾는 문제로 greedy하게 해결할 수 있다.
Thm 11.1
MST문제를 풀기 위한 방법은 다음과 같다: (i) $e_1$을 G의 가장 작은 weightfkrh gkwk. (ii) $e_2, e_3, …, e_{n-1}$을 $e_i$와 cycle을 가지지 않는 간선들 중에 가장 작은 edge들로 골라가면 원하는 spanning tree를 만들 수 있다.
