Path and Cycles
1. Connectivity
trail: a walk in which all the edges are distinct
path: a trail in which the vertices are distinct
cycle: trail or path in which initial vertex and final vertex are the same
Thm 5.1
If G is a bipartite graph, then each cycle of G has an even length.
Thm 5.2
Let G be a simple graph on n vertices. If G has k components, then the number m of edges of G satisfies $n-k \leq m \leq (n-k)(n-k-1)/2$
lower bound는 가능한 적은 edge를 가지고 있다고 가정해서 증명
upper bound는 complete graph라고 가정해서 증명
Corollary 5.3
Any simple graph with n vertices and more than (n - 1)(n - 2)/2 edges is connected.
Thm 5.2에 k = 1 즉 graph가 1개의 component로 이루어졌을 경우를 가정해 대입하면 증명할 수 있다.
disconnecting set: a connected graph G is a set of edges whose removal disconnects G cutset: no proper subset of which is a disconnecting set bridge: a cutset with only one edge e > edge connectivity $\lambda$(G): minimum number of edges that we need to delete in order to disconnect G *G is k-edge connected if $\lambda$(G) ≥ k.*
separating set: set of vertices whose deletion disconnects G; cut-vertex: a separating set contains only one vertex v vertex connectivity $\kappa(G)$: the size of the smallest seperating set in G. G is k-connected if $\kappa(G)$ ≥ k.
2. Eulerian graphs
Eulerian: closed trail이 graph G의 모든 edge를 포함하면 connected graph G는 Eulerian이다. 해당 trail은 Eulerian trail이다.
semi-Eulerian: Eulerian graph가 아닌 G가 semi-Eulerain이려면 모든 edge를 포함하는 trail이 있어야 한다.
LEMMA 6.1
If G is a graph in which the degree of each vertex is at least 2, then G contains a cycle.
v1에 v2를 연결하고, v2의 degree는 적어도 2인데 cycle을 만들지 않기 위해 v3에 연결하고… 마지막 vertex vn도 degree가 2가 되어야 하는데, 어느 곳에 연결해도 cycle을 형성한다. 즉 모순이라는 것을 증명하면 된다.
LEMMA 6.2
A connected graph G is Eulerian if and only if the degree of each vertex of G is even.
⇒ 나가는 곳이 있으면 들어오는 곳이 있다.
⇒ G의 edge 숫자에 대한 귀납법으로 증명
COROLLARY 6.3
A connected graph is Eulerian if and only if its set of edges can be split up into disjoint cycles.
직관적으로, vertex에서 나가는 것이 있으면 돌아오는 것이 있어야 eulerian graph가 되고, 나가는 것이 2개 이상인 경우가 있을 때 여러 cycle이 생길 수 밖에 없다.
COROLLARY 6.4
A connected graph is semi-Eulerian if and only if it has exactly two vertices of odd degree.
오일러 그래프에서 원점으로 돌아오고 나서 어딘가로 한번 더 가야된다면, semi-Eulerian이 된다.
semi-Eulerian은 모든 edge를 커버하고 나서 어딘가로 더 가야된다는 것인데, 그러려면 두 개의 vertex는 odd degree여야 한다.
Thm 6.5
Let G be an Eulerian graph. Then the following construction is always possible and produces an Eulerian trail of G. Start at any vertex u and traverse the edges in an arbitrary manner, subject only to the following rules:
(i) erase the edges as they are traversed, and if any isolated vertices result, erase them too; (ii) at each stage, use a bridge only if there is no alternative.*
지워나가는 vertex가 bridge를 만드는데, 해당 bridge가 graph를 disconnect 시키는 graph가 아닐 경우 odd degree를 가진 vertex가 3개 이상이 됨을 증명한다.
3. Hamiltonian graphs
Hamiltonian graph: closed trail passing exactly once through each vertex of G semi-Hamiltonian: non-Hamiltonian 중에 path passing through every vertex*
Thm 7.1
If G is a simple graph with n (≥ 3) vertices, and if deg(v) + deg(w) ≥ n for each pair of non-adjacent vertices v and w, then G is Hamiltonian.
non-Hamiltonian graph를 가정하고 contradiction임을 보여 증명
Corollary 7.2
If G is a simple graph with n (> 3) *vertices, and if deg(v) ≥ n/2 for each vertex v, then G is Hamiltonian.
Thm 7.1에서 바로 유도 가능
4. Some algorithms
1) The Shortest path problem
Suppose that we have a ‘map’, in which the letters A ~ L refer to towns that are connected by roads. If the lengths of these roads are as marked, what is the length of the shortest path from A to L?
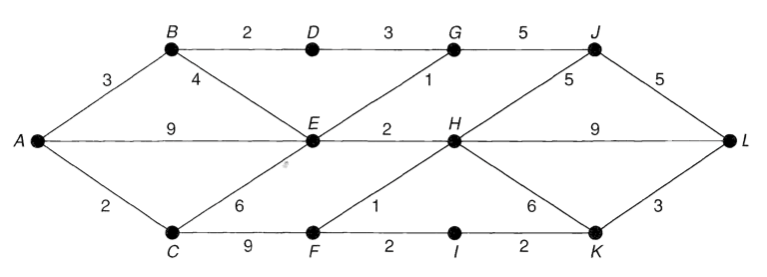
→ 다익스트라 알고리즘
2) The Chinese postman problem
Postman wishes to deliver his letters, covering the least possible total distance and returning to his starting point. He must obviously traverse each road in his route at least once but should avoid covering too many roads more than once.
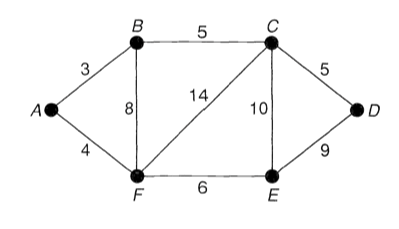
→ non-eulerian을 만드는 vertex B, E를 잇는 shortest path를 찾는 문제
3) The travelling salesman problem
A travelling salesman wishes to visit several given cities and return to his starting point, covering the least possible total distance.
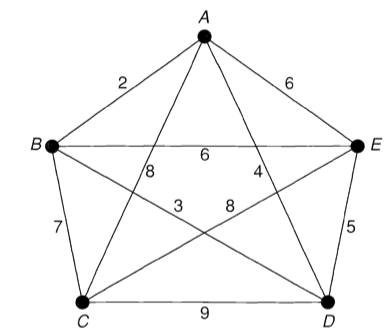
→ Weighted complete graph에서 Hamiltonian cycle of least possible total weight를 찾는 문제.
